Describe Two Anatomical Structures That Strengthen the Hip Joint
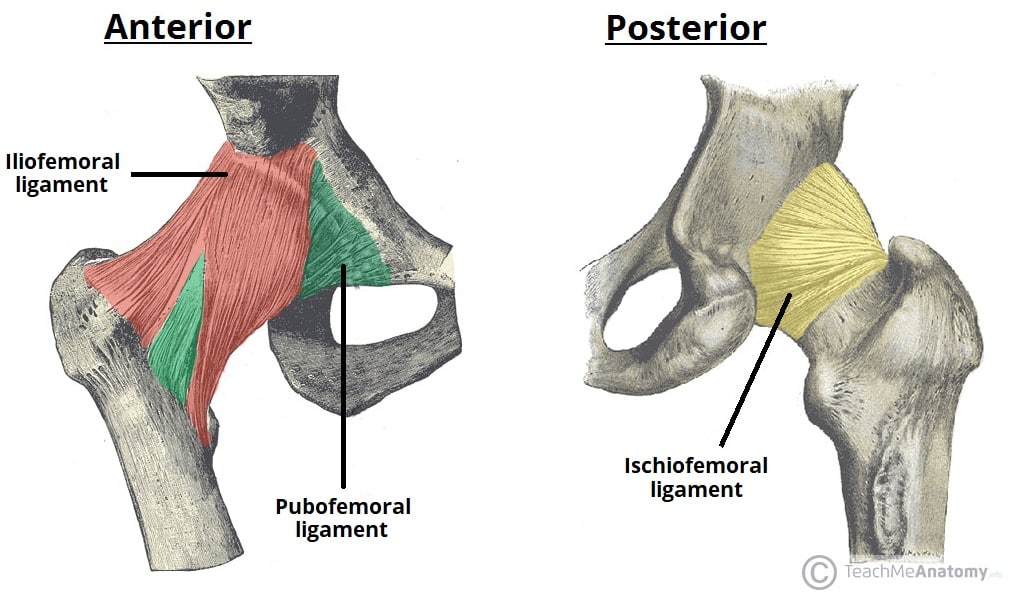
The head of the femur and the cup like acetabulum are covered with articular cartilage. Ischiofemoral ligament - stretches from the body of the ischium to the trochanteric fossa.

Solved The Shoulder And Hip Joints Are Ball And Socket Chegg Com
Finally two groups of important ligaments help add stability.

. Large snugly-fitting joints or deep sockets improve stability hip ball socket 2Ligament number and locationposition Greater the number of ligaments the stronger and more stable a joint is If ligaments are the major stabilizers the joint will not be very stable because Ligament can stretch only 6 of its length before it snaps. Make up the pelvic girdle. The synovial membrane lines the inner surface of the joint capsule and produces synovial fluid.
Knee flexion preloads the quadriceps muscles strengthening its force across the hip. The acetabulum is a cup-like depression located on the inferolateral aspect of the pelvis. Zona orbicularis - extends from the anterior inferior iliac spine surrounds the neck of the femur and ends where it started.
Quadriceps and hamstrings are the muscle which is seen on the knee helps to strengthen and gives flex to the joint of the knee. The six types of synovial joints are pivot hinge condyloid saddle plane and ball-and socket-joints Figure 943Figure 943 Types of Synovial Joints. This ligament helps limit excessive extension and adduction internal rotation.
The gluteal muscle are seen to position the knee. Both the hip joint and the shoulder joint are ball and socket joints. The hip joint consists of an articulation between the head of femur and acetabulum of the pelvis.
Most movements have an opposite movement also known. DrAkramJaffar Dislocation of the hip joint Stability of the hip joint. -Glenohumeral ligamentthree binds of fibers that appear as thickenings in the ventral wall of the joint capsule and extend from the edge of the glenoid fossa to the lesser tubercle and the anatomical neck of the humerus-Transverse humeral ligamentruns between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus.
Located on the back of the hip joint this ligament connects the ischium to the femur. Running from the front of the pelvis to the femur this is the strongest ligament in the body. A ring of fibrocartilage acetabular labrum and a cylindrical joint capsule reinforced with ligaments including the iliofemoral ligament pubofemoral ligament and ischiofemoral ligament help keep the articulating surfaces of the hip together.
Joint Capsule and Bursae. There is two type of meniscus which is known as medial and lateral menisci also act as the absorber in the bone of femur and the tibia. Synovial joints are subdivided based on the shapes of the articulating surfaces of the bones that form each joint.
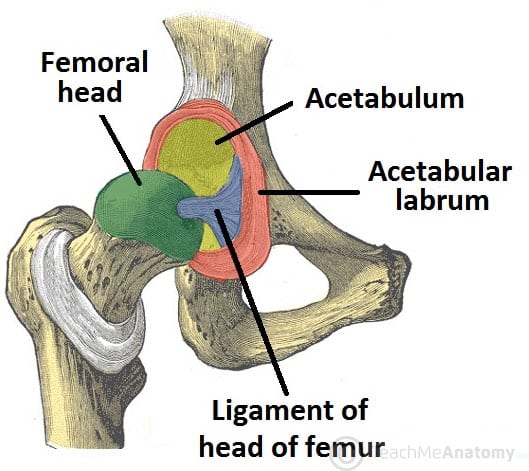
Its cavity is deepened by the presence of a fibrocartilaginous collar the acetabular labrum. Deepens the socket Hip joint-Acetabuler labrum increases the depth of the joint cavity and helps seal synovial fluid-Ligamentum teres attaches to the fovea captious. Muscles contract to produce movement at joints and the subsequent movements can be precisely described using this terminology.
Ilium Ischium pubis The pelvic girdle is also referred to as the pelvis Joints in the pelvis girdle. The rectus femoris flexes the hip joint and extends the knee joint. Identify poses that stretch and strengthen the muscle groups surrounding the hip.
The joint capsule is a fibrous sheath which encloses the structures of the joint. It prevents the thigh from excessive inner rotation and adduction at the hip joint. The terms used assume that the body begins in the anatomical position.
It is formed by the circular fibers of the hip joint capsule. The articular fossa is filled with fat and covered by synovial membrane. Anatomical complications of a fracture or dislocation.
March 22 2017 Anatomy Lower Limb dislocation of hip joint hip joint capsule hip joint ligaments hip joint movements hip joint relations Hip joint type nerve and arterial supply of hip joint. 2 Describe the attachment of capsule of. The position of the knee during hip flexion does affect its ability to generate force at the hip.
Does not rely on muscular support iliofemoral ligament strongest in body joint capsule strengthened by ligaments pubfemoral ischiofemoral iliofemeral. Sacrum Coccyx Two hip boneswhich are comprised of. The cartilage in the acetabulum is in a horseshoe or lunate shape.
Shoulder Joint Glenohumeral joint-Greatest ROM 5 Major ligaments of stability. Anatomy related to correct relocation and alignment. It extends from the anatomical neck of the humerus to the border or rim of the glenoid fossaThe joint capsule is lax permitting greater mobility particularly abduction.
Right and left sacroiliac joints Symphysis pubis Lumbosacral joint Lippert p247 Function of Pelvis Supports the weight of the body through the vertebral column and passes that force onto the hip bones. The head of femur is hemispherical and. The rectus femoris provides its strongest contribution to hip flexion when the knee is flexed.
Flexors extensors adductors abductors and rotators. Structures of the Hip Joint Articulating Surfaces. The anatomy of displacement or deformity.
By the end of this course you will be able to. Contents show Advertisements. Types of Synovial Joints.
Anatomical terms of movement are used to describe the actions of muscles upon the skeleton. Hip Joint synovial ball and socket femur articulates with the actabulum socket deepened by acetabular labrum very congruent joint. The six types of synovial joints allow the body to move in a variety of ways.
Which structures help keep the articulating surfaces of the hip together. Furthermore a strong fibrous capsule the medial patellar and lateral patellar retinacula patellar tendon iliotibial tract lateral side and longitudinal fibers of fascia lata medial side all serve to strengthen the joint. Describe the general anatomy and the structure of the hip.
1 Name the type and articular surface of Hip Joint. Demonstrate how the shape of your hip joint will affect movement and asana practice. Imaging anatomy features and how to differentiate from epiphyseal lines.
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy

No comments for "Describe Two Anatomical Structures That Strengthen the Hip Joint"
Post a Comment